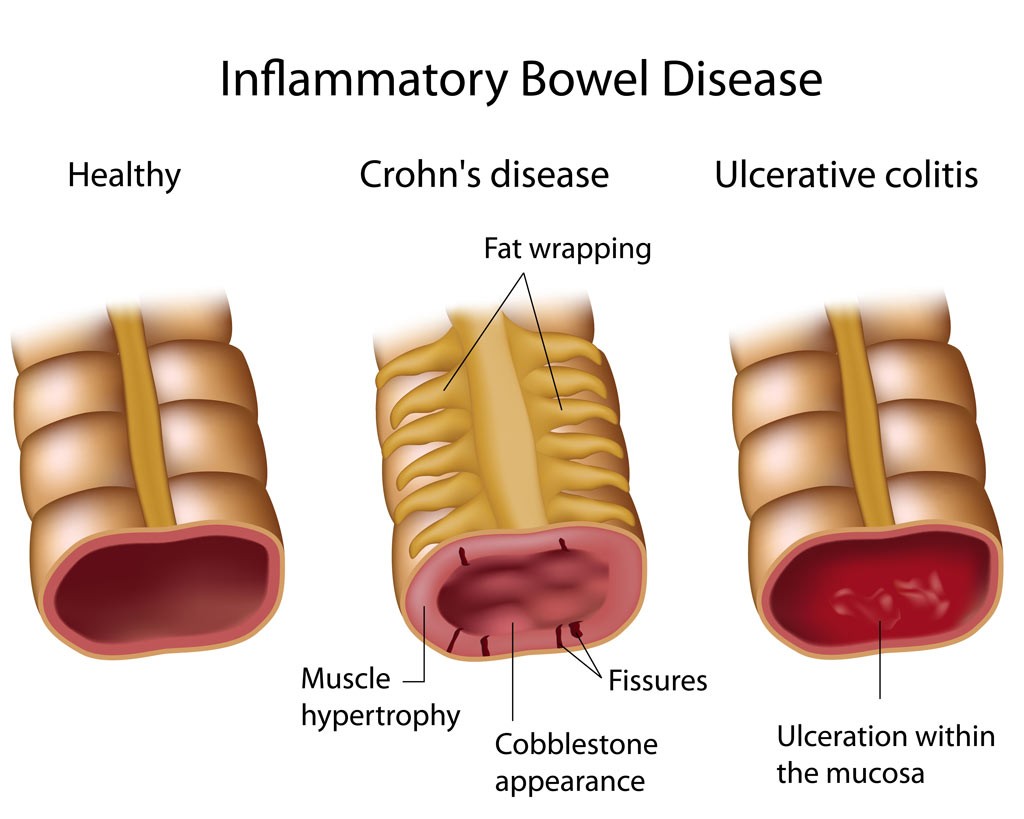
 Crohn’s disease is a form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that involves the end of the small intestine (ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (colon). Crohns may also involve any part of the digestive system from the mouth to the end of the rectum (anus). Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a related condition that is limited to the colon. The symptoms of these two illnesses are quite similar, but the areas affected in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract) are different.
Crohn’s disease is a form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that involves the end of the small intestine (ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (colon). Crohns may also involve any part of the digestive system from the mouth to the end of the rectum (anus). Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a related condition that is limited to the colon. The symptoms of these two illnesses are quite similar, but the areas affected in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract) are different.
Crohn’s disease is a form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that involves the end of the small intestine (ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (colon). Crohn’s may also involve any part of the digestive system from the mouth to the end of the rectum (anus). Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and is a related condition that is limited to the colon. The symptoms of these two illnesses are quite similar, but the areas affected in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract) are different. IBD is a condition that causes chronic inflammation of the intestines. IBD occurs in children as a result of genetic and environmental factors. For reasons that are not yet clearly understood, the child’s immune system becomes abnormally active against his or her own intestines.
The symptoms of Crohn’s disease often depend on the severity of the disease and the location of the disease in the bowel. Often children with Crohn’s disease have periods of severe symptoms followed by periods of remission (no symptoms). Most children experience a combination of the following.
Children with Crohn’s disease can have complications such as stunted growth, weak bones and delayed puberty. Other symptoms can occur from complications of the disease.
The exact causes of Crohn’s disease are not completely known, but it thought to be the result of of genetic, immune system, and environmental factors.
IBD is diagnosed by finding specific changes to the intestines. To see these changes, tissue samples from the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine are obtained, using a procedure called an upper and lower endoscopy with biopsy. This procedure is done while the child is under anesthesia. If symptoms and medical history indicate Crohn’s Disease, Dr. Davé will schedule an endoscopy.
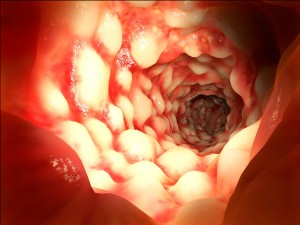
Crohn’s Disease Cobblestone Mucosa
Because Crohn’s is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease, the goal of treatment is reduction in symptoms and remission. Periods of remission can last for weeks or years, and there is no way to predict when symptoms will return. When Crohn’s disease is active, treatment focuses on controlling inflammation and relieving symptoms of pain, diarrhea and fever. Medication is often the first step in treating children with Crohn’s disease.
When medications fail to control the symptoms of Crohn’s, surgery to remove part of the bowel may be necessary.
It is important for children managing Crohn’s to have a healthy lifestyle. They should exercise regularly and eat a healthy diet. Most children with Crohn’s disease are able to like an active life and participate in school, activities and sports when the disease is treated properly.
If you would like more information about gastrointestinal (GI) digestive disorders and nutrition in children, please contact Dr. Mona Dave’s Frisco Office or Request Appointment Here.